In the group of diseases of the musculoskeletal system of degenerative-dystrophic origin, gonarthrosis of the knee joint ranks first.
Gonarthrosis or osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a disease accompanied by a slow destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joint with the involvement of the entire joint in the pathological process, including ligaments, synovium, lsubchondral bone and other parts of the joint.
Under the influence of various factors, such as infectious diseases (colds, flu, typhus, tuberculosis, syphilis, tonsillitis and others), injuries, functional congestion of the joint (for example, in athletes, workersperforming hard physical labor, ballet dancers) there is a violation of the trophism (nutrition) of the cartilage tissue of the knee joint, as a result, the cartilage becomes thinner and destroyed, sometimes until complete disappearance.
Who is at risk? First of all, osteoarthritis of the knee joint is likely to "win" women over forty, they suffer from it twice as often as in the strong half of humanity. Additionally, the risk increases in women who tend to be overweight or obese.
But overall, knee osteoarthritis is a disease of the elderly. And there is a simple explanation for this. As you know, cartilage tissue contains about 70-80% water, due to which it absorbs well. In addition, at a young age, the "restorative" cells of chondrocytes are actively working. With age, the amount of moisture begins to decrease, and as a result, the ability to cushion the joint worsens, the cartilage becomes dry, brittle and cracks, and the existing chondrocytes do not have time torepair the damage. In many ways, this explains the occurrence of gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
Causes of the disease
Predisposing factors are excess weight, physical inactivity, chronic joint damage or systematic joint strain injuries, alcohol abuse, chronic stress, previous or existing knee joint disease, such as:
- arthritis of the knee,
- sprain, partial or complete rupture of ligaments,
- intra-articular fracture of the femur or tibia,
- metabolic disorders, such as gout, and a number of other pathological conditions.
Very often it is not possible to establish a specific cause of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, in this case they speak of a combined cause, that is, knee osteoarthritiswas the result of several illnesses at the same time.
Also, the disease, for the sake of onset, is usually divided into two forms: primary and secondary.
Primary osteoarthritis is caused by age and associated factors, such as:
- Professional predisposition,
- Overweight,
- Obesity,
- Varicose veins of the lower limbs.
The cause of secondary knee osteoarthritis may be a previous injury to the knee (fracture, rupture of the ligamentous apparatus), called post-traumatic arthritis of the knee joint. The same reason can be a previous infectious disease or inflammation of the knee joint.
Symptoms
Signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint do not appear overnight, the development of the disease occurs gradually and often takes several months or even years. Pain that is permanent and increases with physical activity - walking, running, going down or up stairs, etc. - come to the fore. Another characteristic symptom of this disease is the presence of crepitus in the joint, it may be a crackle or crackle in the knee.
Very common manifestations of knee osteoarthritis are also:
- a local (the joint is hot to the touch) or general temperature increase,
- presence of joint swelling,
- increasing its volume,
- difficulty of movement,
- deformation of the joint followed by curvature of the limb.
As the disease progresses, when the cartilage tissue is completely destroyed, the body has no choice but to start defending itself. This is manifested by the proliferation of bone tissue on the bones that form the joint in the form of "spines" (osteophytes), there is deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint. The exudate appears in the joint cavities.
Depending on the size of the osteophytes and the degree of deformation, there are several degrees of knee osteoarthritis:
- Grade 1 knee osteoarthritis.Patients experience stiffness and mild pain in the joint in the morning or when sitting or standing for a long time. There is no deformation of the joint at this stage, the mobility is completely preserved. An x-ray reveals a small osteophyte.
- Grade 2 gonarthrosisPainful sensations appear, not only in the morning, but also after prolonged exertion, the joint is deformed, the joint surfaces are enlarged, which also increases the volumeof the joint, flexion is difficult, tightening is felt when performing movements. The x-ray shows a pronounced osteophyte, the joint space is not changed.
- Grade 3 gonarthrosis.The manifestations are the same as in the second degree, only the symptoms become more pronounced. The pain is permanent, it does not go away even with rest and sleep. The function of the joint is almost completely lost, patients can neither bend the leg nor straighten it. As a result, lameness occurs, movement becomes possible only with crutches or outside help. There is a pronounced deformation of the knee joint. On the x-ray, a slight narrowing of the joint space is determined.
- There is also a fourth stage, in which there is complete immobility in the affected joint with further deformity. On the x-ray, the phenomena of sclerosis of the subchondral bone and a significant narrowing of the joint space are determined.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
In order to get good treatment results, you need to seek help from a qualified rheumatologist, and if he is not there then a therapist, as they know how to cure osteoarthritis of theknee joint. In no case should you try to treat it yourself, it can only make an already no better situation worse. Before starting treatment, it is extremely important to make the correct diagnosis, as correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment.
The treatment of knee osteoarthritis is a rather long process and depends on a number of factors (type of osteoarthritis, cause of osteoarthritis, degree of disease). Treatment is complex and includes drug and non-drug therapy, and in some cases surgical treatment is indicated.
Drug treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee joint is primarily aimed at relieving the main manifestations of the disease, such as:
- Pain;
- Inflammation of joint and periarticular tissues.
In addition to relieving the symptoms of the disease, drugs are used to:
- joint tissue repair,
- improving trophism and blood circulation,
- strengthen the body's defenses,
- elimination of allergic reactions.
Various non-narcotic pain relievers are used to relieve pain symptoms, in rare cases narcotic pain relievers are prescribed for a short time. Most often, drugs are used in the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They have a combined anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect.
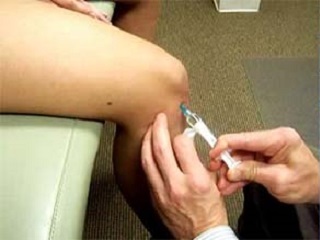
Chondroprotectors are used to restore cartilage tissue and improve joint mobility. The drugs stimulate the activity of cartilage cells - chondrocytes, and help them repair tissue. The intra-articular insertion of the head protectors gives a good effect. In recent years, a new effective product based on hyaluronic acid has appeared. For its action, this medicine is called "liquid prosthesis". When injected into a diseased joint, this drug forms a protective film on damaged cartilage and gradually restores the joint's normal lubricating characteristics.
Muscle relaxants are used to relieve muscle spasms, in addition to a relaxing effect, they have a positive effect on blood circulation in the affected joint.
Manual and physical therapy are widely used from the non-drug methods of treating knee osteoarthritis. The most important are magnetotherapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis and massage, device traction (joint extension) and others. Recently, methods such as laser therapy, cryotherapy (exposure to liquid nitrogen) have come into the practice of treating osteoarthritis. Along with physiotherapy, exercise therapy for osteoarthritis of the knee joint also gives good effect. Lfk is the use of various physical exercises for therapeutic purposes.
Gymnastics for osteoarthritis of the knee joint
At the onset of the disease, physical activity on the diseased joint should be minimized. You should not jog, jump, lift weights, walk fast, or squat. Knee joint osteoarthritis exercises can only be done after treatment, under the supervision of your doctor.
It is necessary to choose exercises that help strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the affected knee joint, but at the same time do not lead the joint to excessive mobility. In other words, the exercises should be with minimal dynamic activity. It is useful to do exercises to stretch ligaments and joint capsules. The rules are the same, the exercises are performed smoothly, without effort.
When performing a gymnastic exercise, it is important to follow certain rules:
- Don't exercise in pain
- If the exercise causes pain, it should be replaced with a milder one.
Massage for osteoarthritis of the knee has a beneficial effect on restoring the functions of the knee joint. At the site of exposure, blood vessels dilate, blood circulation improves, and metabolism is accelerated. Massage procedures improve lymphatic flow, which, in turn, helps remove residual inflammation. Massage strengthens the muscular system, increases the flow of oxygen to them, improves gas exchange, normalizes their tone and increases plasticity.
Diet for osteoarthritis of the knee
Recently, medical specialists discovered that there was no direct relationship between the incidence of knee osteoarthritis and nutrition. However, an indisputable fact is that the development of osteoarthritis is strongly influenced by the presence of excess weight in a person. If the cause of the disease was precisely excess weight, then it is obvious that nutrition for osteoarthritis of the knee joint should be aimed at a gradual decrease in body weight. This will require a regime change and a regime change. Foods should be lower in calories, fried foods and foods high in fat should be excluded from the diet. Eat more vegetables, fruits, and fluids.
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
In order for the joints to remain healthy for as long as possible, it is necessary to regularly practice physical culture and gymnastics, but do not get too carried away by this, so that it does not lead to overloading the joints. Swimming gives the best effect and minimum stress on the joints. If professional sports are involved, joint protection should be used. It is useful to alternate physical activity and rest, you should not stay still for long.
Following all of these simple rules, along with a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition, will not allow osteoarthritis of the knee joint to ruin anyone's life.





































